ELR’s premium electric power steering system is designed to provide excellent feedback while saving fuel. Dual-pinion, rack-mounted electric power steering system with premium ZF steering gear. A combined electric motor and sensing unit monitors steering angle and delivers appropriate assist to the steering gear at all times, correcting for crowned road surfaces and cross-winds. This helps reduce driver fatigue.
In driver-selectable Sport mode, ELR’s steering gear provides increased on-center sharpness and steering sensitivity for dynamic steering. In the more relaxed Tour mode, it allows precise control with less driver steering efforts.
ELR’s continuous damping control monitors sensors throughout the vehicle, vehicle speed and the driver’s input, and adjusts damping accordingly for each 20-inch wheel every two milliseconds to maintain optimal vehicle ride control over varying road surfaces and profiles. This reduces and controls vehicle roll, pitch and vertical motions for a flat “sky-hook” ride performance, and instantly responds to cornering maneuvers by automatically adjusting the dampers to a firmer level for superior handling and stability. When driving on smooth roads, the dampers are automatically adjusted to the softest setting to provide increased isolation and ride comfort.
An isolated four-mount front cradle contributes to the ELR’s overall quietness, noise and vibration performance, and ride-and-handling dynamics. Specifically tuned mounts are tailored to the engine’s inherent torque axis, decreasing the transfer of vibration and noise into the cabin.
The newly developed generation of brushless motors provides the assist calculated by the electronic control unit with high precision in any driving condition. The latest materials enable high efficiency with extremely small size. In addition, the drive was optimized with respect to noise performance and torque ripple for the requirements of an electric power steering system.
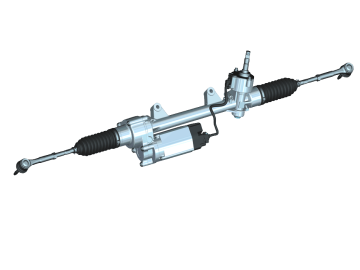 |
| ZF Dual-pinion Electric Power Steering(EPS) |
SYSTEM COMPONENTS
Motor
 |
| ZF Power Motor |
The newly developed generation of brushless motors provides the assist calculated by the electronic control unit with high precision in any driving condition. The latest materials enable high efficiency with extremely small size. In addition, the drive was optimized with respect to noise performance and torque ripple for the requirements of an electric power steering system.
Torque Sensor
 |
| ZF Torque Sensor |
The torque sensor measures the torque applied by the driver at the steering wheel. Based on this, the control unit calculates the steering assistance for the motor.
Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
 |
| ZF Electronic Control Unit |
The ECU houses all the components – 32-bit microcontroller with on-chip flash memory and RAM, as well as the output stage for the motor – in what is a fully integrated, hermetically sealed unit. In order to ensure optimum response, the electronic control unit has all the relevant information permanently “in view”, including stored vehicle data as well as current operating parameters (such as vehicle speed, engine status or steering speed).
Second Pinion
The servo unit on a second pinion is a further superb option, designed for mid-size or upper midsize cars. The installation of the servo unit on the second pinion enables the physical separation of the sensor and the drive unit. The fact that the drive pinion ratio is independent of the steering ratio creates the opportunity for a performance-optimized configuration. The increase in system performance is in the order of 10 -15 %. And superb crash safety is guaranteed thanks to optimum use of the available installation space. By allowing a rotation of the servo unit of 360° about the axes of the rack and the drive pinion, the position of the servo unit can be defined to fit the particular application.
Other Component
Second Pinion
 |
| ZF Dual-pinion Steering Sytem *first pinion is steering pinion *second pinion is drive pinion |
The servo unit on a second pinion is a further superb option, designed for mid-size or upper midsize cars. The installation of the servo unit on the second pinion enables the physical separation of the sensor and the drive unit. The fact that the drive pinion ratio is independent of the steering ratio creates the opportunity for a performance-optimized configuration. The increase in system performance is in the order of 10 -15 %. And superb crash safety is guaranteed thanks to optimum use of the available installation space. By allowing a rotation of the servo unit of 360° about the axes of the rack and the drive pinion, the position of the servo unit can be defined to fit the particular application.
Other Component
- Tie Rod : Completes the connection between the steering rack and the wheel.
- Bellows : It protects the inner joints from dirt and contaminants.
- Steering Racks : The steering rack produces linear motion from an applied torque to the pinion.
- Housing : Cover steering rack.
- Sensor Cable : Send data from torque sensor to ECU.
SYSTEM OPERATION
As soon as the driver turns the steering wheel, sensors
register the corresponding steering torque and steering speed with absolute
precision.
The registered data are used to
calculate the required steering assistance and, based on the calculated
results, to control the electric motor.
In the final step, the motor
transmits the optimum servo torque – via worm gear or recirculating ball gear –
to the steering column (EPSc), second pinion (EPSdp) or steering rack (EPSapa)
in the mechanical rack and pinion steering system.
If the vehicle power supply
fails, the driver can continue to steer the vehicle, due to the mechanical
connection between the steering wheel and the steered wheels.
 |
| Flow Diagram of System Operation ZF Dual-pinion EPS |
BENEFIT OF TECHNOLOGY
- The electric power steering system can save weight, space and fuel.
- The benefit of electric power steering is its simplicity. While a lot of design work and technology goes into the electric system itself, it simplifies vehicle assembly and frees up space in the engine compartment.
- Electric systems don't need fluid or hoses. Vehicle assembly and repair is also simplified because hoses don't need to be connected and air evacuated out of hydraulic systems.
- For drivers, the big benefit of electric power steering has to be fuel economy. Because the systems only uses power when the wheels are turned compared to hydraulic systems that pump fluid all the time the engine is running.












